Benefits of Physical Activity
- Benefits of Physical Activity
- Cardiovascular Training
- Muscle Strength and Muscular Endurance Training
- Flexibility
Research shows that a total amount of 150 minutes (2 hours and 30 minutes) a week of moderate-intensity aerobic activity, such as brisk walking, improves both physical and mental health. An easy way to remember this is 30 minutes at least 5 days a week. Don’t have 30 minutes? That's ok, it doesn't have to be done all at once. You can break down your activity into as little as three 10 minute periods of activity which is just as beneficial to your overall fitness as one 30-minute session. This is achievable and SPARTANfit Fitness & Wellness Program is here to help you!
The Benefits of Physical Activity:
- Improves energy and decreases fatigue
- Promotes better sleep
- Helps fight depression, tension, anxiety, and stress
- Provides opportunities to meet and connect with new people
- Improves mood and self-esteem
- Improves cardiovascular fitness
- Increases muscle strength and endurance
- Increases metabolism and helps to maintain weight
- Reduces your risk for chronic disease and other adverse health outcomes
Note: Although physical activity is safe for most people, health experts suggest that you talk to your doctor before you start an exercise program.
The American College of Sports Medicine recommends the following Aerobic Activity for substantial health benefits for Adults:
- 150 minutes (2 hours and 30 minutes) each week of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity (such as brisk walking or tennis).
OR
- 75 minutes (1 hour and 15 minutes) each week of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity (such as jogging or swimming laps).
- An equivalent combination of moderate- and vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity.
- Gradual progression of exercise time, frequency and intensity are recommended for best adherence and least injury risk.
- People unable to meet these minimums can still benefit from some activity.
What is the difference between Moderate-intensity and Vigorous-intensity Physical Activity?
Intensity refers to the rate at which the activity is being performed or the level of the effort required to perform an activity or exercise. It can be thought of "How hard a person works to do the activity".
The intensity of different forms of physical activity varies between people. The intensity of physical activity depends on an individual’s previous exercise experience and their relative level of fitness. Consequently, the examples given below are provided as a guide only and will vary between individuals.
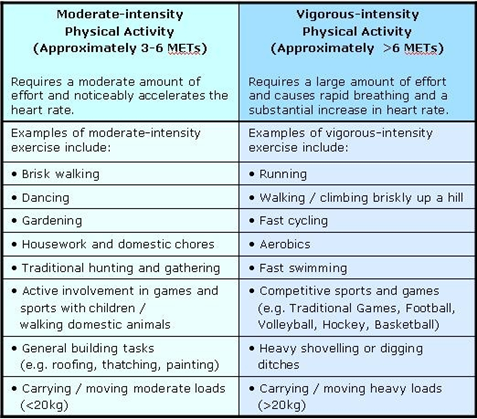
Metabolic Equivalents (
METs ) are commonly used to express the intensity of physical activities. MET is the ratio of a person's working metabolic rate relative to their resting metabolic rate. One MET is defined as the energy cost of sitting quietly and is equivalent to a caloric consumption of 1kcal/kg/hour. It is estimated that compared with sitting quietly, a person's caloric consumption is three to six times higher when being moderately active (3-6METs ) and more than six times higher when being vigorously active (>6METs ).Adapted from: WHO's "What is Moderate-intensity and Vigorous-intensity Physical Activity?"
Muscular strength (how much you can lift) is the maximum amount of force a muscle can produce in a single effort. Muscular endurance (how long you can lift) is the ability of the muscle to continue to perform without fatigue. Together they provide the power and capacity of muscle and connective tissue elements to undergo stress and strain in order to achieve a variety of activities by pulling, pushing, stretching, extending and flexing different joints of the body. Muscular strength and endurance training
The benefits of muscular strength and muscular endurance training include:
- Reduces body fat and increases lean body mass (muscle mass)
- Helps to keep bones dense and strong
- Increases energy levels
- Helps you to maintain correct posture
- Increases metabolism and helps to maintain weight
- Helps you to perform everyday tasks such as climbing stairs and lifting objects
- Reduces your risks of being injured
- Increases the strength of tendons and ligaments
- Adults should train each major muscle group two or three days each week using a variety of exercises and equipment.
- Very light or light intensity is best for older persons or previously sedentary adults starting to exercise.
- Two to four sets of each exercise will help adults improve strength and power.
- For each exercise, 8-12 repetitions improve strength and power, 10-15 repetitions improve strength in middle-aged and older persons starting to exercise and 15-20 repetitions improve muscular endurance.
- Adults should wait at least 48 hours between resistance training sessions.
Flexibility is needed to perform everyday activities with relative ease. Flexibility is primarily due to one’s genetics, gender, age, body shape and level of physical activity. As people grow older, they tend to lose flexibility. This is usually as a result of inactivity but is partially due to the aging process itself. The less active you are, the less flexible you are likely to be. Furthermore, regrettably, flexibility training is often neglected. As with cardiovascular activity and muscle strength and endurance training, flexibility will improve with regular training.
The Benefits of Flexibility training:
- Allows greater freedom of movement and improved posture
- Increases physical and mental relaxation
- Releases muscle tension and soreness
- Reduces the risk of injury
- Adults should do flexibility exercises at least two or three days each week to improve range of motion.
- Each stretch should be held for 10-30 seconds to the point of tightness or slight discomfort.
- Repeat each stretch two to four times, accumulating 60 seconds per stretch.
- Static, dynamic, ballistic and proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) stretches are all effective.
- Flexibility exercise is most effective when the muscle is warm. Try a light aerobic activity or a hot bath to warm the muscles before stretching.

